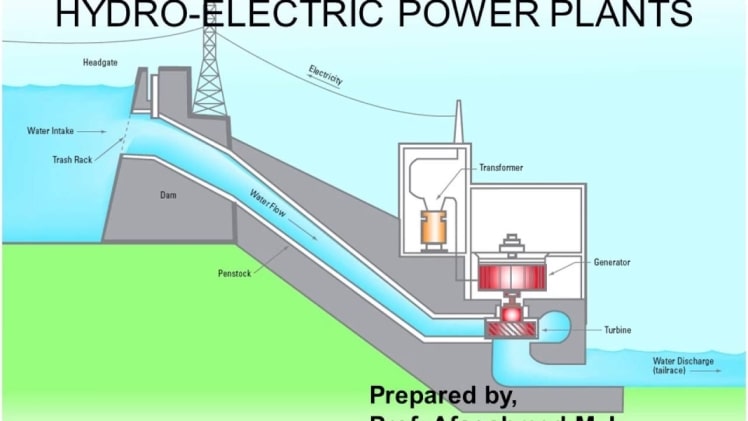
Components of A Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectricity (conserved force in water sources) production is among the cleanest means of creating electricity. By 2012, hydroelectricity plants produced around 16% of total global energy output. Hydropower is the most extensively utilized renewable energy source. This is a dynamic source of power, and the expense of generating electricity is quite low. The architecture and fundamental elements of the hydropower generation plant are discussed in this article.
What is Hydropower Plant?
A hydropower facility generates electricity by using the hydraulic force of water. The electricity generated by this facility is known as hydroelectricity. Hydropower accounts for around 16% of total global power consumption.
There are various sorts of hydroelectric plants based on their qualities. However, some key components are required for any hydroelectric plant, and these are discussed below.
Components of a hydropower plant:
Forebay:
A forebay is indeed a hydroelectric plant basin region where fluid is temporarily kept before entering the intake room. The amount of water stored in the forebay is determined by the area’s water usage. It is also employed whenever the intake volume requirement is low.
Intake structure:
The intake mechanism draws liquid out from forebay and sends these into the penstocks. There are several sorts of intake structures accessible, and also the kind of intake structure chosen is dependent on several local factors.
Trash racks are one of the most significant components of the intake system. Trash racks are supplied at the penstock’s entry to catch garbage in the water.
Penstock:
Penstocks are long, slanted pipelines that transport water from an intake system or water storage to the rotors. They operate under some pressure, therefore rapid locking or releasing of penstock valves might result in overpressure on the penstocks.
Excluding the fact that a penstock is comparable to standard pipe, are engineered to withstand the water hammer impact. To alleviate this force, a thick wall is given for short-length pipework, while a surge tank is installed with long-length penstocks. Penstock fabrication is used to protect the penstock from damage.
Surge tank:
The surge tank is just a collection reservoir installed at a point upon a long piping system or penstock to collect the flow that is refused when the duct line is abruptly stopped by a regulator installed at the other side. As a result, a surge tank assuages the water pipes of the extra pressure created by its shutting, so removing the strong overpressure effect.
It is accomplished by allowing into the holding tank a considerable volume of water that would usually have flowed out from the piping system but rebounds towards the tank owing to the closing of the tube end.
Turbines:
The hydraulic motor receives fluid from its penstock. This turbine is structurally connected with a generator that generates electricity. The kinetic force of the water powers the turbine, which moves the power source. Water turbines are classified into two kinds: impulse turbines and reaction turbines. High heads are handled by impulse turbines, whereas low and mid heads are handled by reaction turbines.
Powerhouse:
The powerhouse is a structure designed to safeguard hydraulic and electrical systems. In general, the base or superstructure created for the generator house supports the whole infrastructure.
Some devices, such as draft pipes, scroll covering, etc, are attached within the base as it is being laid in the situation of reaction rotors. As a result, the ground is built in large dimensions.
Whenever it relates to the architecture, generators are installed on the lower floors, beneath which vertical rotors are installed. Horizontal rotors are available in addition to the generator. A monitoring room is available on the first or upper floors.
Draft tube:
When reaction turbines have been utilized, a draft pipe is required to link the turbine output with the tailrace. This draft tube progressively increases in diameter, allowing water to release through into the return line at a suitable speed. Outlet valves are placed at the bottom of the inlet pipe and can be blocked during major repairs.
Tailrace:
The movement of fluid from the rotors to the channel is referred to as a tailrace. This is preferable if the electricity station is placed closer to the watercourse. However, if it is positioned farther from the flow, a canal for conveying water through the stream must be built.
Final thoughts:
Hydroelectric power is an established technique with well-proven technologies and a high level of dependability. A hydropower facility is made up of civil, industrial, and electromechanical engineering components




